Augmented reality technology enhances our perception of the real world by overlaying digital information. This technology has been gaining momentum in recent years, with applications in gaming, education, and marketing. This blog post will answer the most basic question- how does augmented reality work ?, including the different types of AR, the hardware and software required, and some examples of how it is currently being used.
Table of Contents
How Does Augmented Reality Work- The Details
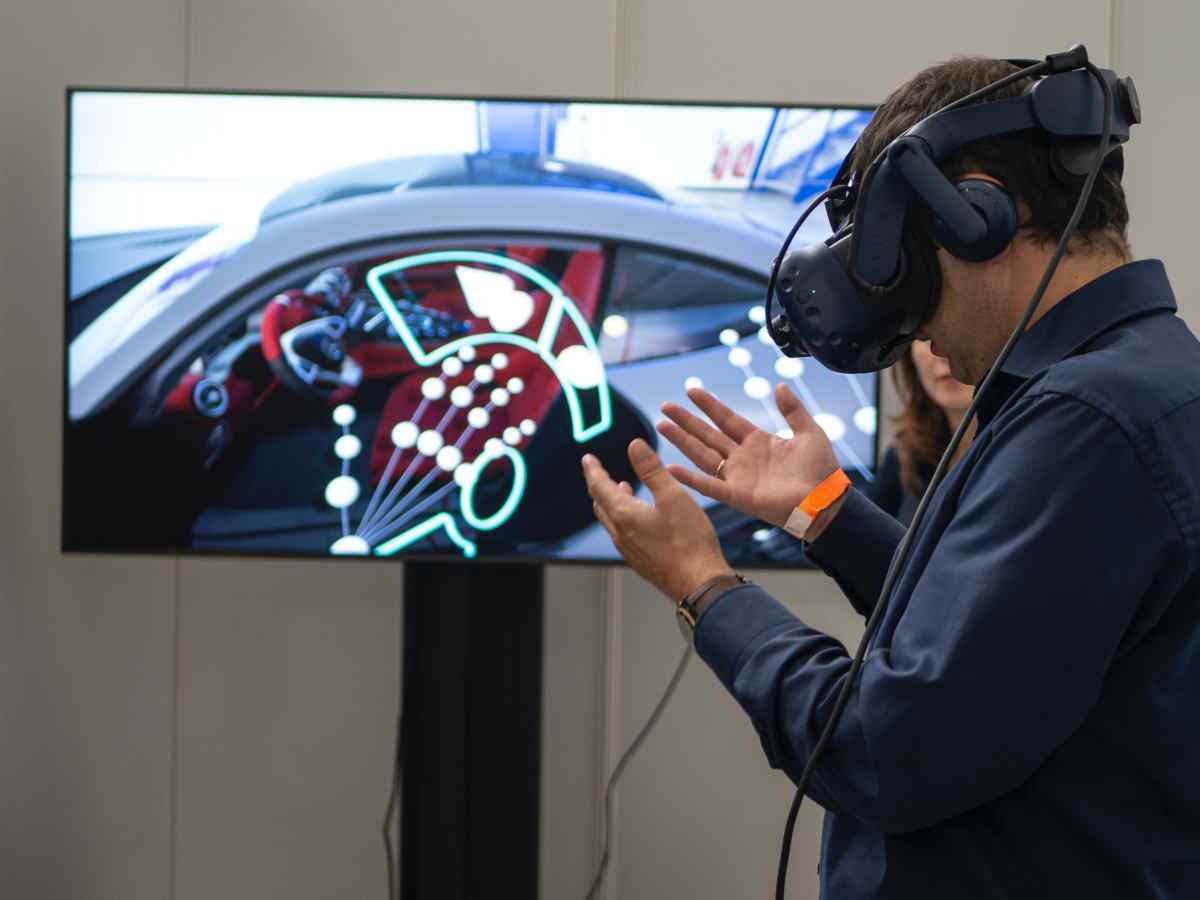
Augmented reality overlays the virtual world on the real world. The first of many questions one could ask in that case is, how does augmented reality work?
Augmented reality uses a device’s camera, sensors, and processing unit to track and map the user’s environment and overlay digital information on top of it. The process of creating an AR experience typically involves the following steps:
Tracking and Mapping
The first step in creating an AR experience is to track and map the user’s environment. This is done using the device’s camera and sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, to gather information about the environment. This information is then used to create a 3D map of the environment, which determines the position and orientation of the device with the environment.
Recognition
Once the environment has been tracked and mapped, the AR software must recognize the relevant objects or images. This step is particularly important for marker-based AR, where a specific image or object is used to trigger the overlay of digital information.
Overlay
AR software overlays digital information on top of the real-world view once the environment has been tracked and mapped and the relevant objects have been recognized. The overlay can be interactive and responsive to the user’s movements and actions, allowing for a more immersive experience.
Display
The final step is to display the augmented reality experience to the user. This is typically done using the device’s display, such as a smartphone or tablet screen, or head-mounted displays (HMD) like Microsoft Hololens or Magic Leap.
Hardware and Software
The use of AR requires hardware and software components, as discussed below.
Hardware
A device with a camera, sensors and a processing unit is required to use augmented reality. The most common devices used for AR include smartphones, tablets, and head-mounted displays (HMDs), such as the Microsoft Hololens and the Magic Leap.
Smartphones and tablets are widely available and are typically used for marker-based AR experiences, such as the popular mobile game Pokemon Go. These devices use the camera and sensors to track the marker and display the overlay of digital information.
Head-mounted displays are typically used for more advanced and immersive AR experiences. These devices are worn on the head and have built-in cameras, sensors, and displays, allowing for a more immersive experience.
In addition to smartphones, tablets and HMDs, other specialized hardware devices can be used for AR. For example, AR-enabled smart glasses and smart contact lenses are under development, which would allow for a more subtle and natural AR experience.
Software
The AR application is what the end-user interacts with to create AR applications.
AR apps and games are typically created using code-based platforms like Unity and no-code platforms like PlugXR. They use Software Development Kits (SDKs) like Vuforia, ARKit, and ARCore. These platforms are also loaded with powerful features like cloud editors, no-code drag & drop to help creators build immersive applications faster.
Hardware and software are important components of augmented reality. As technology continues to improve, we expect to see more advanced hardware and software for augmented reality to enable more immersive and natural AR experiences.
Use Cases of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality has several applications, including but not limited to the following:
1. Gaming
One of the most popular uses of augmented reality is in gaming. Games like Pokemon Go, Ingress, and Harry Potter: Wizards Unite uses AR to create an immersive gaming experience that combines the real and virtual worlds. Players can explore their surroundings to find and catch virtual creatures, complete tasks, and interact with other players. This enhances the overall gaming experience and encourages players to get out and explore the real world.
2. Marketing
Augmented reality is used to create interactive and immersive brand experiences. For example, Ikea’s Place app allows users to see how furniture would look in their home before making a purchase. In contrast, Lowe’s Holoroom allows customers to design and visualize home improvement projects. By using AR, companies can give customers a realistic and engaging experience with their products, making it more likely that they will make a purchase.
3. Healthcare
Augmented reality assists with surgeries, training and patient education. AR-enabled visualization technologies allow surgeons to overlay patient-specific information on top of real-time images during surgeries, enabling them to see important details that would be otherwise invisible. Also, with the help of AR, medical students can practice complex procedures and surgeries in a simulated environment, which is much safer than practicing on live patients.
4. Architecture and Construction
AR can assist architects and builders in design and construction. Architects can create virtual models of buildings and walk through them in 3D, allowing them to identify potential problems before construction begins. Similarly, builders can use AR to overlay digital information on the physical construction site, allowing them to see how the finished project will look and identify potential issues.
5. Military and Law Enforcement
AR can enhance the situational awareness and decision-making of military and law enforcement personnel. AR-enabled head-mounted displays can provide real-time information to soldiers and officers in the field, such as maps, thermal imaging, and communication links. This allows them to make better decisions and operate more effectively in dangerous and challenging environments.
As AR technology advances, it will become more accessible, reliable, and user-friendly, driving more people to adopt it daily.
Conclusion
Augmented reality enhances the perception of reality by overlaying digital information onto it. It can be used in various applications, such as gaming, education, and marketing. As technology continues to improve, we expect to see more and more augmented reality applications in our daily lives.